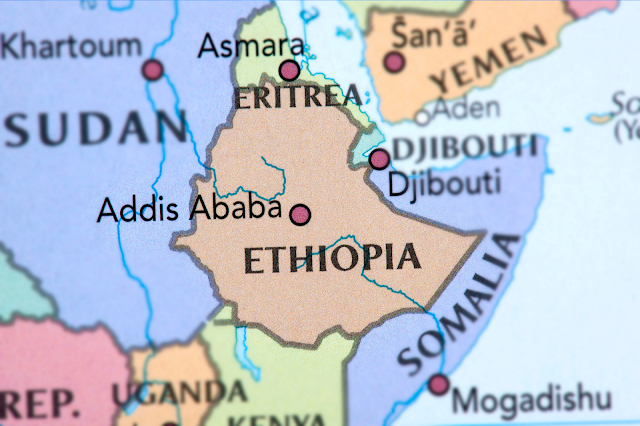
Eritrea, located in the Horn of Africa, has a long and complex history shaped by ancient civilizations, colonial rule, armed struggle, and post-independence challenges. It has been influenced by African, Middle Eastern, and European cultures due to its strategic location on the Red Sea.
Ancient and Medieval Eritrea
Early Civilizations (Prehistory – 1st Century CE)
Eritrea’s earliest inhabitants were hunter-gatherers and later Cushitic-speaking agriculturalists.
The Land of Punt (c. 2500 BCE), a trading partner of ancient Egypt, is believed to have been partly located in present-day Eritrea.
The D’mt Kingdom (c. 1000–400 BCE) flourished in what is now Eritrea and northern Ethiopia, developing iron tools, writing systems, and trade networks.
Aksumite Empire (100–940 CE)
The Aksumite Empire, centered in Ethiopia and Eritrea, was a major power controlling Red Sea trade routes.
Christianity was introduced in the 4th century CE under King Ezana, making the region one of the first in Africa to embrace the religion.
After the fall of Aksum due to climate change and Islamic expansion, Eritrea fragmented into smaller chiefdoms and sultanates.
Islamic Influence and the Medieval Period (10th–19th Century)
From the 7th century, Arab traders introduced Islam along the Eritrean coast, leading to the rise of the Dahlak Sultanate (a powerful trading center).
Various local rulers, including the Ottoman Turks (16th century), controlled Eritrea’s coastal regions due to their importance in Red Sea trade.
Colonial Rule (1885–1941)
Italian Colonization (1885–1941)
In 1885, Italy invaded Eritrea, defeating local forces and making it an Italian colony in 1890.
Italians built modern infrastructure, railways, and cities (such as Asmara) but oppressed native Eritreans.
Eritrean soldiers (ascari) served in Italy’s invasions of Ethiopia (1896 and 1935–1936).
Mussolini’s fascist government expanded control, but Italian rule ended after British forces defeated Italy in WWII (1941).
British Administration and Federation with Ethiopia (1941–1961)
Britain ruled Eritrea from 1941 to 1952, treating it as a UN trust territory.
Eritreans debated their future: some wanted independence, while others sought union with Ethiopia.
In 1952, the UN federated Eritrea with Ethiopia, granting it autonomy under Emperor Haile Selassie.
However, Ethiopia dissolved Eritrea’s autonomy in 1962, annexing it as a province—sparking armed resistance.
Eritrean War of Independence (1961–1991)
Beginnings of the Armed Struggle (1961–1974)
In 1961, the Eritrean Liberation Front (ELF), led by Hamid Idris Awate, launched a guerrilla war against Ethiopian rule.
In the 1970s, a splinter group, the Eritrean People’s Liberation Front (EPLF), led by Isaias Afwerki, became dominant.
The Ethiopian military government (Derg), led by Mengistu Haile Mariam (1974–1991), responded with brutal counterinsurgency tactics, including massacres and bombings.
EPLF Victory and Eritrean Independence (1991–1993)
In 1991, after 30 years of war, the EPLF defeated Ethiopian forces, entering Asmara and effectively liberating Eritrea.
In 1993, Eritreans voted overwhelmingly (99.8%) for independence in a UN-backed referendum.
Eritrea became officially independent on May 24, 1993, with Isaias Afwerki as its first president.
Post-Independence Challenges (1993–Present)
Early Years and War with Ethiopia (1998–2000)
Initially, Eritrea focused on rebuilding after decades of war.
However, border tensions with Ethiopia led to the Eritrean-Ethiopian War (1998–2000), which killed over 100,000 people.
A peace agreement was signed in 2000, but tensions persisted until a 2018 peace deal restored diplomatic relations.
Domestic Challenges: One-Party Rule and Human Rights Issues
Isaias Afwerki has remained in power since 1993, ruling as an authoritarian leader.
No elections have been held since independence.
Eritrea has been accused of:
Political repression (banning opposition parties and free press).
Mandatory military service, which can last indefinitely.
Severe human rights abuses, leading to mass emigration (thousands flee to Europe yearly).
Regional Conflicts and Foreign Relations
Eritrea has been involved in regional conflicts, including:
Supporting rebel groups in Ethiopia, Somalia, and Sudan.
A border dispute with Djibouti (2008).
Sending troops to Ethiopia’s Tigray War (2020–2022).
Recent Developments (2018–Present)
In 2018, Eritrea and Ethiopia signed a peace deal, ending two decades of hostility.
The UN lifted sanctions on Eritrea, but domestic repression continues.
Many Eritreans still face economic hardship, limited freedoms, and military conscription.
Conclusion
Eritrea’s history is marked by ancient civilizations, colonial rule, a long independence struggle, and post-independence authoritarianism. Despite gaining independence through great sacrifice, its government remains highly repressive, with ongoing human rights concerns and regional conflicts.
The future of Eritrea depends on whether political reforms, economic growth, and international cooperation can bring about a more democratic and prosperous nation.
Kindly share this post if you find value in it. Thanks for your support.
You can Watch this program on YouTube
P.S. In case you want to, feel free to reach out to me. If you need advice on your plans and ideas, and how to manage your time and resources, drop me a message here or email me at sopiensofgod@gmail.com, and we’ll arrange a call.
Read Next: Are You Clear About What You Want This Year?
Will you like to write a book – share your story, ideas or knowledge in a book, now it’s easier than ever. In 3 weeks, your book will be written and published. Send a message to: bookminds247@gmail.com.
Get books on Amazon: Amazon Books
Check out our website: Wordflixx Publishers
If you want customized songs for you or your loved ones' birthday, wedding, or any ceremony, Iseay music got you. Contact @ sopiensofgod@gmail.com
You can also check out these posts:
1. Making 2025 Your Best Year Yet
2. What to Do When You Are Confused
Kindly drop your comments here:
Kindly share this post if you find value in it. Thanks for your support.
You can Watch this program on YouTube
P.S. In case you want to, feel free to reach out to me. If you need advice on your plans and ideas, and how to manage your time and resources, drop me a message here or email me at sopiensofgod@gmail.com, and we’ll arrange a call.
Read Next: Are You Clear About What You Want This Year?
Will you like to write a book – share your story, ideas or knowledge in a book, now it’s easier than ever. In 3 weeks, your book will be written and published. Send a message to: bookminds247@gmail.com.
Get books on Amazon: Amazon Books
Check out our website: Wordflixx Publishers
If you want customized songs for you or your loved ones' birthday, wedding, or any ceremony, Iseay music got you. Contact @ sopiensofgod@gmail.com
You can also check out these posts:
1. Making 2025 Your Best Year Yet
2. What to Do When You Are Confused
Kindly drop your comments here:





No comments:
Post a Comment